
Troubleshooting your Fluent Bit Configuration with Calyptia Cloud
Troubleshooting your Fluent Bit Configuration with Calyptia Cloud
Note: Calyptia Cloud has been integrated into Calyptia Core. Some of the specifics in this article may be different in Core. You can create a free Calyptia Core account.
Introduction
Calyptia Cloud is our hosted solution optimizing observability pipelines utilizing open source Fluent Bit or Fluentd. It provides a unified, vendor-neutral control plane for visualizing, managing, and monitoring your observability pipelines. It allows users to focus on gaining the most insights and value out of their data pipelines in cloud-native environments.
Creating an account is free and lets you connect and monitor up to five Fluent Bit or Fluentd installations.
Today, however, we will be looking at one particular feature of Calyptia Cloud that we have heard from our users adds a lot of value: the Config Visualizer. This tool helps you to
Visualize the observability pipeline you are trying to set up.
Troubleshoot your Fluent Bit configuration files by validating them against common errors
All you have to do is copy and paste your config file. You don’t even need to have a running installation of Fluent Bit to use the tool, making it particularly useful both for beginners as well as seasoned Fluent Bit users trying to debug a complex pipeline configuration.
In this post, I’ll demonstrate how to use the Config Visualizer feature of Calyptia Cloud with several examples of increasing complexity.
Getting Started
First, you’ll need a free Calyptia Cloud account:
Create an account or log in to your existing account
Once you have logged in, navigate to the Config Visualizer tool.
And you should see the tool.
Sample: Sending Log Files to S3 and Splunk
We’ll start with an easy one. Copy the configuration below, paste it into the editor, and hit the “Validate” button. You can also provide a name for the configuration, although it is not required.
[INPUT]
Name tail
path /home/ec2-user/test/*.log
tag sample.1
[FILTER]
name grep
match *
regex log ^(\[ERROR\]).*
[OUTPUT]
Name s3
Match *
bucket eb-co-calyptia-cf-template
region us-east-1
total_file_size 50M
upload_timeout 1m
compression gzip
s3_key_format /fluent-bit-logs/$TAG/%Y/%m/%d/%H/%M/%S
use_put_object On
[OUTPUT]
Name splunk
Match *
host 18.118.66.88
port 8088
splunk_token xxxxxxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxxxxxxxxx
splunk_send_raw On
tls on
tls.verify offHere we are taking log files from an EC2 instance, filtering them to retain only those that contain an error message, and sending them to both S3 and Splunk for storage and analysis.
Your screen should look something like this.
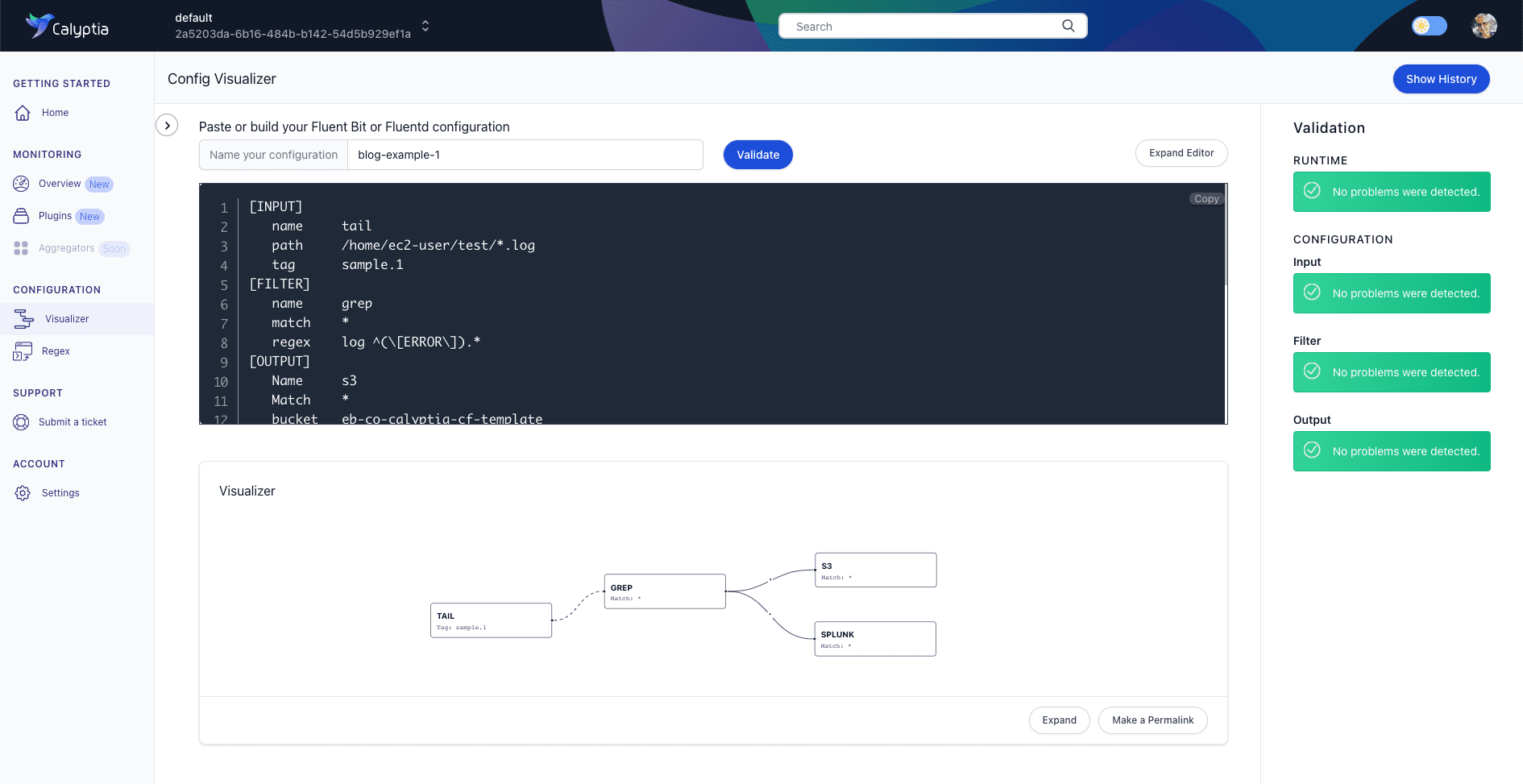
First, on the right-hand side of the screen, we can see that our config file passed validation checks without any issues being detected.
Beneath the editor is the visualization of our observability pipeline showing our data source, Fluent Bit’s filtering of the data, and its dual destinations.
Everything looks good!
Troubleshooting Your Observability Pipeline Configuration
As your observability pipelines grow more complex with multiple tags, filters, and parsers applied to deliver the exact data you need to all of the places it needs to go, it is easy to make mistakes. Calyptia Cloud can help you troubleshoot your pipeline configuration.
Paste the configuration below into the Calyptia Cloud configuration editor and hit Validate.
[SERVICE]
Flush 1
Log_File /var/log/fluentbit.log
Log_Level error
Daemon off
Parsers_File parsers.conf
HTTP_Server On
HTTP_Listen 0.0.0.0
HTTP_Port 2020
[INPUT]
Name tail
Tag test.file
Path /var/log/apache2/error.log
DB /var/log/apache2_error.db
Path_Key filename
Parser apache2
Mem_Buf_Limit 8MB
Skip_Long_Lines On
Refresh_Interval 30
[INPUT]
Name tail
Tag kube.*
Path ${PATH}
Parser docker
DB /var/log/flb_kube.db
Mem_Buf_Limit 7MB
Skip_Long_Lines On
Refresh_Interval 10
[FILTER]
Name record_modifier
Match *
Record logtype nginx
Record hostname ${HOSTNAME}
Record service_name Sample-App-Name
[FILTER]
Name kubernetes
Match kube.*
Kube_URL https://kubernetes.default.eab.cluster.local:443
Merge_JSON_Log Off
[OUTPUT]
Name nrlogs
Match *
apiKey ${API_KEY}This time when we hit validate, we can see an error in our Kubernetes filter: “configuration option: merge_json_log not found for filter plugin: kubernetes.”
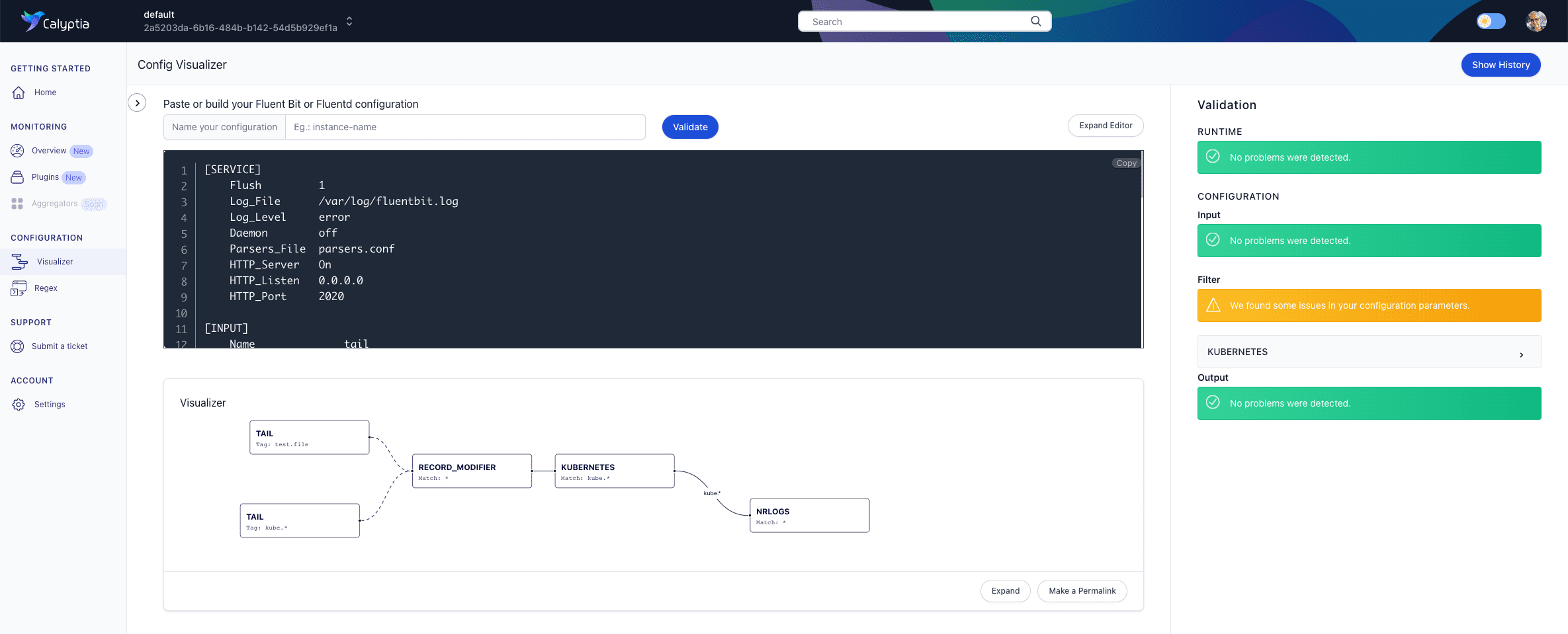
The error appears to be in this line:
Merge_JSON_Log OffAfter a quick review of the official Fluent Bit documentation for the Kubernetes filter, we discover that we have misused the key. It should be:
Merge_Log OffMake that change in the editor, and the error message should disappear.
Note: As we are using Fluent Bit configs in this tutorial. Merge_JSON_Log is the correct key phrasing for the Fluentd Kubernetes plugin. If we were testing Fluentd configuration files that line would have passed, although others would have failed because of differences between the two projects.
Another Troubleshooting Example
Let’s try one final example that reveals a different way to diagnose an issue. To follow along, copy, paste, and validate this sample:
[INPUT]
Name tail
Tag task-status-es
Path /var/log/containers/htc-agent-erik*.log
Parser docker
DB /var/fluent-bit/state/flb_container.db
DB.locking true
Mem_Buf_Limit 50MB
Skip_Long_Lines On
Skip_Empty_Lines On
Refresh_Interval 10
Rotate_Wait 30
storage.type filesystem
Read_from_Head True
[FILTER]
name grep
match task-status-es
regex $log['node'] update_status
[FILTER]
Name nest
Match task-status-es
Operation lift
Nested_under log
Remove_prefix log
[FILTER]
Name nest
Match task-status-es
Operation lift
Nested_under message
Remove_prefix message
[FILTER]
Name record_modifier
Match task-status-es
Remove_key node
Remove_key level
Remove_key stream
Remove_key time
[OUTPUT]
Name es
Match task-status-es
AWS_Region us-east-1
AWS_Auth On
tls On
Host vpc-grid-monitoring-4qvdh2mbu4qvdhzuceuh2cke.us-east-1.es.amazonaws.com
Port 443
Logstash_Format On
Logstash_DateFormat %Y%m%d
Logstash_Prefix grid-tasks
Trace_Error On
Trace_Output Off
Id_Key $task_id
Write_Operation upsert
Retry_Limit 10
[OUTPUT]
Name cloudwatch_logs
Match task-status-se
region us-east-1
log_key log
log_group_name /aws/containers/ebledsoe/application
log_stream_prefix ${HOST_NAME}-
auto_create_group true
log_retention_days 1
extra_user_agent container-insights
Retry_Limit FalseThe file didn’t trigger any warnings, indicating that it is formatted correctly.
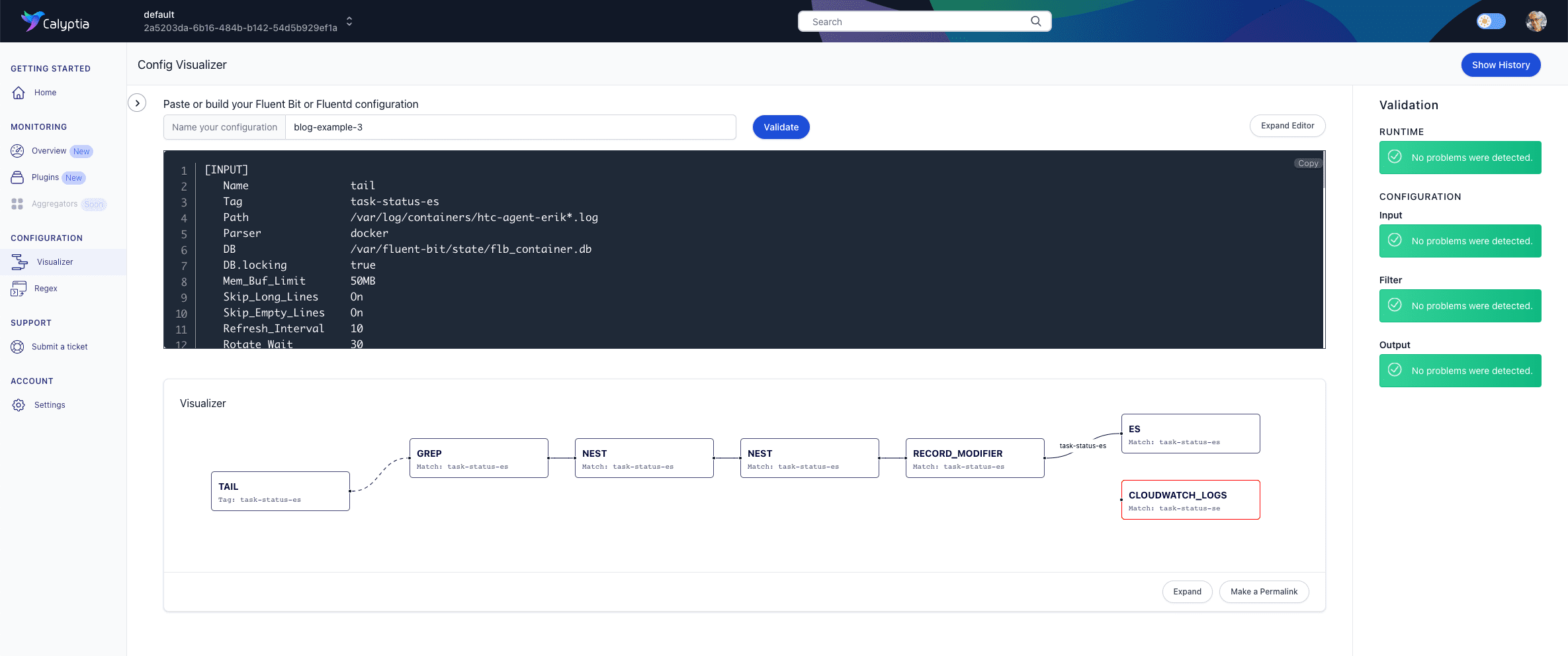
However, if you look at the visualization of our pipeline, you’ll notice that one of our outputs, cloudwatch_logs, is not connected, and its orphaned status is indicated by its red border.
Since we know that in this case, we were simply trying to deliver the same data to two separate outputs, the problem is probably in the Match key/value pair. A quick review of the line reveals a typo in the value. Reverse the final two letters (se >> es), and the file should now be fine.
Limitations
Calyptia Cloud won’t catch every error you may make. It won’t, for example, know that you’ve mistyped the IP address of your host. But we hope that you find it a useful tool.
Next Steps
If you haven’t already, sign up for your free Calyptia Cloud account. In the coming weeks, we’ll be posting more tutorials, including one on using Calyptia Cloud to monitor your running Fluent Bit instances.
You may also want to check out Calyptia’s full range of Fluent Bit-based services and products for the enterprise, including:
Calyptia Core — a Kubernetes solution that simplifies data collection, aggregation, and routing at scale
Calyptia for Fluent Bit — a Long Term Support edition of Fluent Bit for enterprises that require predictable upgrades and an SLA
Calyptia Cloud — a hosted solution for validating, visualizing, and optimizing your Fluentd and Fluent Bit-based observability pipelines
About Calyptia
Named a Cool Vendor in Observability and Monitoring for Logging and Containers by Gartner® for 2022, Calyptia is a leader in solutions for enterprise observability and the creator and primary maintainer of the Fluent Bit open source project. With over a billion deployments, Fluent Bit is the industry-standard open-source engine for enterprise observability of logs and metrics, and it is included in major Kubernetes distributions, including Google Kubernetes Engine (GKE), AWS Elastic Kubernetes Service (EKS), and Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS).
You might also like

Statement on CVE-2024-4323 and its fix
We'd like to make sure you’re aware of a security vulnerability (known as CVE-2024-4323) that impacts Fluent Bit versions 2.0.7 through 3.0.3. The latest version of Fluent Bit, version 3.0.4, fixes this issue.
